Decoding Color Printing: The Essential Role of the Three Primary Colors
Introduction
Printing technology is both a science and an art. It's a blending of technical skills and creative instincts. At the heart of this technology lies an enigma, the mystery of color. You may be familiar with the RGB primary colors – red, green, and blue, standard across most digital devices. But when it comes to print technology, it's all about three different primary colors: cyan, yellow, and magenta. These three colors are fundamental to the printing world. However, their role and significance are often undervalued and underestimated. Our article unravels the fascinating world of the three primary colors in printing technology. Educate yourself on why they are used, how they mix to produce different hues, and their overall impact on image quality.
What Are the Three Primary Colors in Printer Technology?
When we talk about primary colors in the context of printer technology, we are specifically referring to three shades:
1. Cyan: A beautiful blend of green and blue hue, Cyan contributes uniqueness to the world of print.
2. Yellow: Similar to the radiant sun's hue, Yellow lends vibrancy and brightness to the print.
3. Magenta: Lying somewhere between purple and red, Magenta adds depth and richness to the color spectrum.
These three colors, Cyan, Yellow, and Magenta (CYM), are the pillars behind 'subtractive color mixing', an essential process that dictates the world of printing. However, we must not forget the partial role of Black (K) which earned print technology the tag of 'CMYK printing'. This particular discussion will revolve mainly around the contribution of the three primary colors.
Elementary knowledge of these colors can be a game-changer in understanding how an array of colors is derived from just three primary ones. So, whether you are an artist, graphic designer, or a technophile, comprehending the working and essence of these colors can be fascinating as well as beneficial.
Why Do Printers Use These Three Primary Colors: Cyan, Yellow, and Magenta?
Printers utilize Cyan, Yellow, and Magenta as the primary colors due to several functional and aesthetic factors involved in the printing process. Their use is central to the so-called subtractive color mixing, a technique unique to printing. Here are the key reasons for their use:
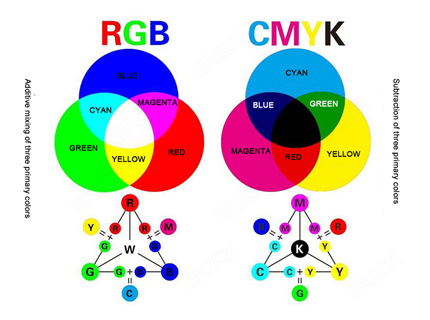
- Subtractive Color Mixing: Unlike the additive RGB system used in digital displays, printers work with a subtractive color model. In this system, Cyan, Yellow, and Magenta are primary colors that, when mixed, subtract wavelengths from white light, thereby creating a range of other colors. If these three are mixed perfectly, the theoretical result should be black. In reality, due to impurities in the inks, the resultant color tends more towards a dull, muddy brown, necessitating the addition of a fourth color—Black (K)—to achieve a richer, deeper black.
- Broad Color Gamut: Cyan, Yellow, and Magenta form a triadic color scheme that has a broader color gamut or range compared to other color trios. This allows printers to reproduce a wider spectrum of colors, thereby enhancing the vibrancy and attractiveness of printed images.
- Accuracy of Hues: Apart from a broad spectrum of colors, these three primary colors also deliver precise hues. This precision translates into clearer, sharper, and more accurate printouts, contributing to an overall improvement in print quality.
- Cost & Efficiency: Using Cyan, Yellow, and Magenta inks is also cost-effective and efficient. It minimizes ink usage while still producing an extensive range of colors and optimized print outputs.
- High-Quality Prints: The combination of these colors ensures high-quality final print products, enhancing image clarity, sharpness, and vibrancy, supporting the provision of professional-grade printing services.
The use of primary colors – Cyan, Yellow, and Magenta, therefore, plays a critical role in the efficiency, aesthetics, and quality of the printing process.
How Does the Color Mixing in Printers Work to Produce Different Hues?
The art and wonder behind how printers utilize cyan, yellow, and magenta to generate a broad spectrum of hues lie within a technique known as halftoning. This ingenious method involves printing minuscule dots of varying colors at such an extent of density that our eyes perceive them as a single, combined color. Here is a step by step breakdown of how this process works:
1. Choice of Primary Colors: The process begins with the three primary printer colors - Cyan, Yellow, and Magenta. These colors form the base for every other color that your printer produces.
2. Halftoning Technique: The halftoning technique is introduced to these colors. This printing method uses tiny dots of the primary colors and varies their density to create new hues.
3. Density Differentiation: The high-density areas appear darker while lower density areas seem lighter. This differentiation can create the illusion of different shades and gradients.
4. Ink Distribution: These tiny dots of ink are placed so close together that the human eye perceives the dots as a unified solid color.
5. Color Perception: The variation in the concentration of each primary color alters the perceived hue, thereby resulting in an extensive palette of shades in the final print.
6. Final Result: The coordinated interplay of these colored dots allows a printer to reproduce a comprehensive range of hues, resulting in vibrant, colorful printouts of various shades.
In conclusion, the key to creating diverse hues in printers is the strategic use of cyan, yellow, and magenta dots, varied in density and concentration. This complex yet elegant mechanism breathes life into our prints and is at the heart of today’s color printing technology.
How Do the Primary Colors Affect Overall Image Quality in Printing?
The pivotal role that primary colors play in determining the quality of print outputs cannot be overstated. They contribute to the color accuracy, vibrancy, and depth of the final images. A careful examination reveals the following aspects of how primary colors can influence print quality :
1. Color Accuracy: The precision of Cyan, Yellow, and Magenta directly impacts the integrity of the printed images. Any discrepancies can lead to a shift in colors, resulting in prints that are unaligned with the original design.
2. Vibrancy & Depth: Proper balance and pure application of primary colors ensure vibrant and deep prints. The vibrancy of color prints can be measured on a scale of 0-100%%, with higher values symbolizing greater vibrancy.
3. Color Range: Primary colors significantly determine the range of colors in printed formats. Inaccurate color representation can lead to a limited color range, making the prints appear dull and lifeless.
4. Clarity & Sharpness: The image resolution is closely linked with the application of primary colors. A precise combination of these primary colors helps maintain a sharp and clear image quality.
5. Print Consistency: Variations in primary colors can cause inconsistent prints, impacting the look and feel of the printing material. A study reveals that a 2% shift in primary color concentration may result in a noticeable difference in printed materials.
To sum up, the accurate replication and distinct application of Cyan, Yellow, and Magenta in printing are critical to delivering high-definition, lifelike, and vibrant printed materials. Hence, understanding these color effects is essential for anyone involved in print-related processes.
Why is Understanding the Printer Colors Essential for Graphic Designers?
Comprehending printer color systems and their complexities is vital for graphic designers. This proficiency has a profound impact on the end products of their resourceful skills. Here's why understanding printer colors is essential for graphic designers:
1. Consistency: A deep understanding of how colors behave when printed versus when viewed digitally assists in maintaining uniformity between the designer's digital creation and the final print.
2. Accuracy: Knowledge of color blending aids graphic designers in creating accurate and consistent color combinations, ensuring that the final output mirrors the original design.
3. Optimization: Understanding printer colors allows designers to enhance their creations for the highest print quality. It gives them the foresight to know how colors might blend or appear in print, thereby allowing for informed design decisions.
4. Brand Identity: Conveying a brand's identity through color is an essential aspect of graphic design. A thorough comprehension of printer colors enables designers to create and maintain color consistency across different print media, ensuring a unified brand image.
Understanding the printer colors - Cyan, Yellow, and Magenta and the role they play in determining the quality and vibrancy of printed output is undeniably crucial in the field of graphic design.
Conclusion
The triad of Cyan, Yellow, and Magenta are pivotal in ensuring accurate and high-quality print results. These three primary colors and their intricate mixing mechanism help bring life to our printing and graphic designs. As the world further evolves into the digital era, the understanding and application of these fundamental colors to align with new age technology stand as a testament to the endurance of these classics.
Related FAQs about what are the three primary colors used in printers
Why do printers use CMYK instead of RGB primary colors?
Printers use CMYK because it's a subtractive process which reduces (subtracts) brightness from white background. RGB is an additive process used by digital devices that adds colours to black background.
How do these primary colors mix to form other colors?
The primary colors mix through a process called halftoning. Tiny dots are printed so densely that the human eye blurs them together, creating different hues.
What role do primary colors play in ensuring accurate print production?
Primary colors - Cyan, Yellow, and Magenta, determine the color accuracy, range, vibrancy & depth, clarity & sharpness of the final printed image, ensuring high-quality print production.