Exploring the World of Printing: An Overview of Printer Types
Introduction
Printing has revolutionized information exchange and continues to evolve rapidly with technology. Printers have assumed different roles and functionalities, each offering unique features and benefits. This article explores the world of printing, giving you an in-depth understanding of various printer types and their uses. It's a comprehensive guide that assists you in choosing the right printer that meets your specific needs.
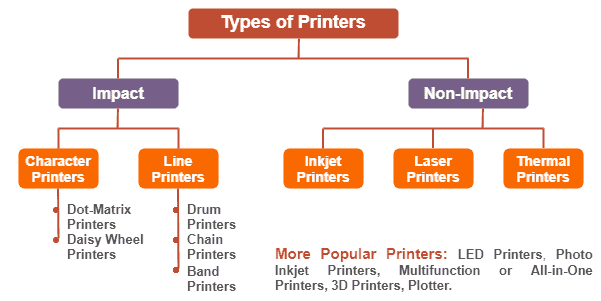
What Are the Different Types of Printers Available?
The Concept of Impact Printers
Impact printers act by directly making contact with the paper by striking an ink-soaked ribbon to produce text or images. These printers are appreciated for their sturdiness and serve as reliable printing solutions.

Printing Methods under Impact Printers:
- Dot Matrix Printer
- Daisy Wheel Printer
- Line Printer
Introduction to Non-Impact Printers
Non-impact printers, in contrast, function without creating any physical contact with the paper. They are known for their ability to deliver clear and precise printouts, making them ideal for producing high-quality prints.
Non-Impact Printer Types:
- Laser Printers: Known for speed and precision, perfect for high volume printouts.
- Inkjet Printers: Ideal for high-quality image printing, suitable for designers and photographers.
- Thermal Printers: Commonly used for printing receipts and barcode labels.
To summarize, the distinction between impact and non-impact printers lies in their functioning. Impact printers use physical contact to create an imprint, while non-impact printers use other methods such as heat or static electricity. Both types have certain contexts where they excel, and your specific environment and requirements will help determine which type of printer is best suited for you.
How Do Laser Printers Work, and What are Their Uses?
Laser printers, popular non-impact printers in the printing world, are renowned for their high-speed operation and premium-quality output. But how exactly do they work? And, what purposes do they serve?
Working of Laser Printers:
Understanding the operation of a laser printer involves four key stages:
1. Charging: The printer drums are intricately charged with static electricity.
2. Writing: A laser pulse shapes the static charge pattern on the drum.
3. Developing: Toner particles, attracted by the charge, adhere to the drum surface.
4. Transferring: The toner is transferred onto paper and fused in place using heated rollers.
Applications of Laser Printers:
Laser printers have a broad spectrum of uses owing to their speed and high-quality outputs. Here are some of the employments:
- Office Use: For large-scale printing requirements and high volume paper outputs.
- Barcode Printing: Known for their precision, they're widely used in barcode printing.
- Label Printing: They offer consistent quality, making them ideal for label printing.
Pros and Cons:
Laser Printers have certain advantages and disadvantages:
Pros:
- Accurate and sharp prints

- Quick printing speed
- Good for high volume printing
Cons:
- High initial cost
- More expensive to maintain
- Consumes more energy
In conclusion, laser printers excel in delivering high-speed and premium quality printouts, making them a popular choice for high-volume printing tasks such as in offices, for barcode printing and generating professional documents.
Understanding Inkjet Printers and Their Applications
Inkjet printers have paved their way into various domains due to their high-quality output and precision. This section unveils the mechanism behind their operation and traces their diverse applications.
Operation of Inkjet Printers
Inkjet printers deliver their output by propelling microscopic droplets of ink delicately onto paper. This intricate process is carried out by the printer’s microscopic nozzles located in the cartridge. The crystal-clear print output is a result of the precise coordination of these droplets.
Notable Applications of Inkjet Printers
Inkjet printers deliver exceptional results when it comes to printing images and graphics. Their high-resolution print output makes them an ideal choice for:
- Home users: They are particularly beneficial for occasional printing tasks including documents, photos, or school projects.
- Graphic designers: Inkjet printers ensure a vivid representation of colors, making them perfect for design printing.
- Photographers: The high-resolution output provided by these printers is excellent for photo printing,
Evaluating Inkjet Printers
Before purchasing an inkjet printer, prospective users should weigh their pros and cons.
Pros:
- High-Quality Output: They deliver sharp and crystal-clear prints, especially for images.
- Variety: Inkjet printers can print on various media types, including glossy photo paper and textiles.
- Cost: They are typically cheaper upfront compared to laser printers.
Cons:
- Speed: They are generally slower in printing compared to their laser counterparts.
- Cost of Ink: While the printers themselves are cheaper, the cost of ink cartridges can add up over time.
- Maintenance: Prone to clogs if not used regularly and require regular cleaning.
Through understanding the core functionality and applications of inkjet printers, potential buyers can evaluate whether this printer type aligns with their needs and preferences.
Delving into the Specialty of Dot Matrix Printers
Dot Matrix printers, when compared to many contemporary printers, occupy a unique niche in the printing world. These printers employ a remarkable mechanism that, while seeming rudimentary to some, remains effective and efficient in settings where multi-part form printing is a necessity. Here's a closer look at the major characteristics of Dot Matrix printers:
How Dot Matrix Printers Work
Dot Matrix printers operate on a pretty basic principle. They use a series of pins, which strike against an inked ribbon. This impact on the paper forms the text or images. As outdated as this may sound to some, remember that this is precisely where Dot Matrix printers gain their advantage - they're able to print on multi-part forms, something that many modern printers struggle to accomplish.
Key Advantages of Dot Matrix Printers
- Multi-part Form Compatibility: Arguably the biggest strength of Dot Matrix printers is their compatibility with multi-part forms, making them ideal for printing invoices, receipts or reports.
- Durability: These printers are built to last. They're robust and reliable, perfect for environments that require constant, heavy printing.
- Cost-Effective: Dot Matrix printers usually involve a low running cost. This is especially beneficial for businesses that need to manage their operating expenses effectively.
Some Cons of Dot Matrix Printers
While Dot Matrix printers come with substantial advantages, they house a few limitations as well.
- Noise: Dot Matrix printers operate with quite a bit of noise. This might not be ideal in a quiet office setting.
- Quality: When compared to modern alternatives like Laser or Inkjet printers, the print quality of Dot Matrix printers doesn't keep up.
Ideal Use Cases for Dot Matrix Printers
Given their distinct operation method and characteristics, Dot Matrix printers are best suited for business or industrial settings. They handle multiple-part forms with ease, proving themselves as an enduring part of the printing arsenal.
Grasping the Concept of Thermal Printers
When it comes to exploring the different types of printers, Thermal printers certainly grab attention with their distinctive operational mechanism and multiple applications.
Thermal printers primarily utilize heat to produce an image or text onto paper. They are categorized into two broad types – Direct Thermal printers and Thermal Transfer printers.
Direct Thermal printers darken the thermal paper by applying heat, making them ideal for short-lived printouts. On the other hand, Thermal Transfer printers use a heated ribbon to produce durable, long-lasting images - a go-to for labels, barcodes, and ID cards.
Below are some significant features are followed by potential benefits and drawbacks of thermal printers:
• Efficiency: Thermal printers work at a high speed, enhancing overall efficiency.
• Quality: They deliver sharp and clear images making them ideal for labels and barcodes.
• Durability: Especially with Thermal Transfer printers, the printed materials are long-lasting and resistant to heat and light.
- Drawbacks:
• Cost: The overall operational costs can be high due to expensive paper and ribbon replacements.
• Lifespan: The lifespan of Direct Thermal printed material is shorter due to sensitivity to light and heat.
Understanding these features can help potential buyers make an informed decision, balancing all factors such as cost-effectiveness, print quality, and durability.
Conclusion
Dot Matrix printers are a type of impact printer that uses pins striking against an inked ribbon to form text or images. They excel in environments requiring multi-part forms printing, such as invoices, receipts, or reports. Due to their robustness and low-cost maintenance, Dot Matrix printers are commonly found in business or industrial settings.
Related FAQs about what are the different types of printers available
Are there any other printers apart from the ones mentioned?
Absolutely, there are several other types of printers not mentioned in this article. These include LED printers, solid ink printers, Dye-Sublimation printers, and 3D printers. Each has its own unique features and applications.
How do I choose the right printer for my needs?
Choosing the right printer depends on your specific needs. Consider factors like printing volume, quality expectations, and types of documents to print. For instance, for high-volume and fast printing, a laser printer is ideal. For high-quality photos, an inkjet printer would be more suitable.
What are the latest technologies in printers?
The latest technologies in printers include 3D printing, wireless connectivity, mobile printing, and advanced security features. Additionally, manufacturers are continuously improving printing speed, energy efficiency, and integration capabilities with other devices.