Understanding 3D Printing: What Materials Are Used And Why?
Introduction
In an age where technology continuously shapes the future, 3D printing stands at the forefront. It's a game-changer, enabling the production of intricate and customized designs. But ever wondered what do 3D printers use to make things? This blog provides an insightful guide detailing the materials used in 3D printing, their applications, and the future of this groundbreaking technology.
What Exactly Is 3D Printing?
3D printing, often referred to as Additive Manufacturing, has revolutionized the technological world with its intriguing capacity to transform digital designs into tangible objects. Here’s a closer look at what this ground-breaking technology entails:
- Process Type: With the ability to construct a physical object from a digital model, 3D printing belongs to the class of 'additive' manufacturing processes. This refers to the method of constructing an object by adding material layer by layer.
- Complexity Handling: A key highlight of this technology is its facility to generate complex geometries that would otherwise be challenging or impossible with traditional manufacturing techniques.
- Material Diversity: The material palette for 3D printings is incredibly broad and dynamic. From plastics, metals, ceramics to an array of other composite materials, 3D printers cater to a vast spectrum of materials, each bringing unique characteristics suited to specific purposes.
- Software Integration: At the heart of 3D printing is a meticulous synchronization with digitally interconnected software. It's this software that detaches the 3D model into plethora of horizontal layers, later guiding the 3D printer in depositing or solidifying the material, layer-upon-layer, towards shaping the intended object.
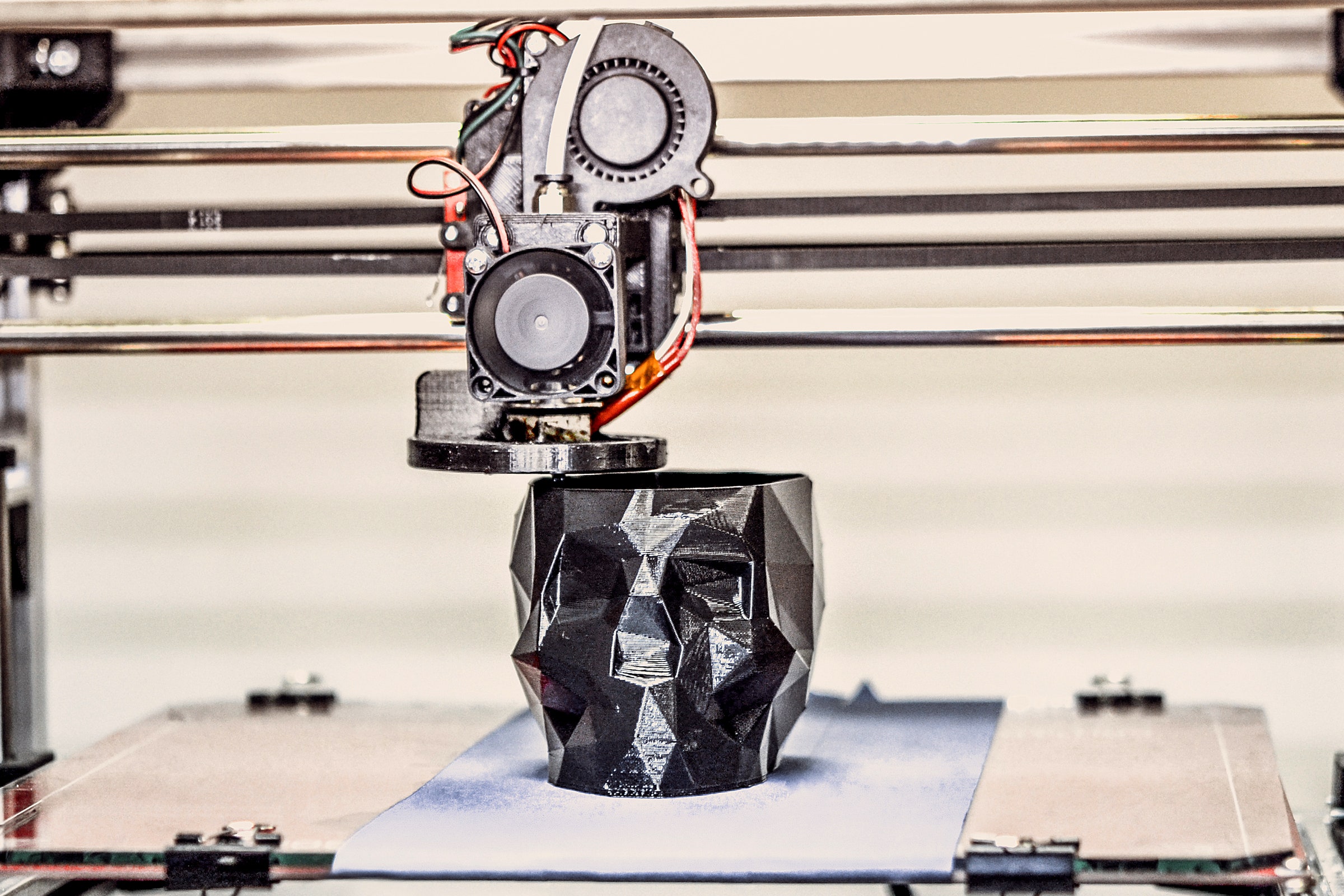
So, 3D printing is not merely a process; it's a holistic integration of digitization, material science and precision that together forge a path for endless innovation and design possibilities.
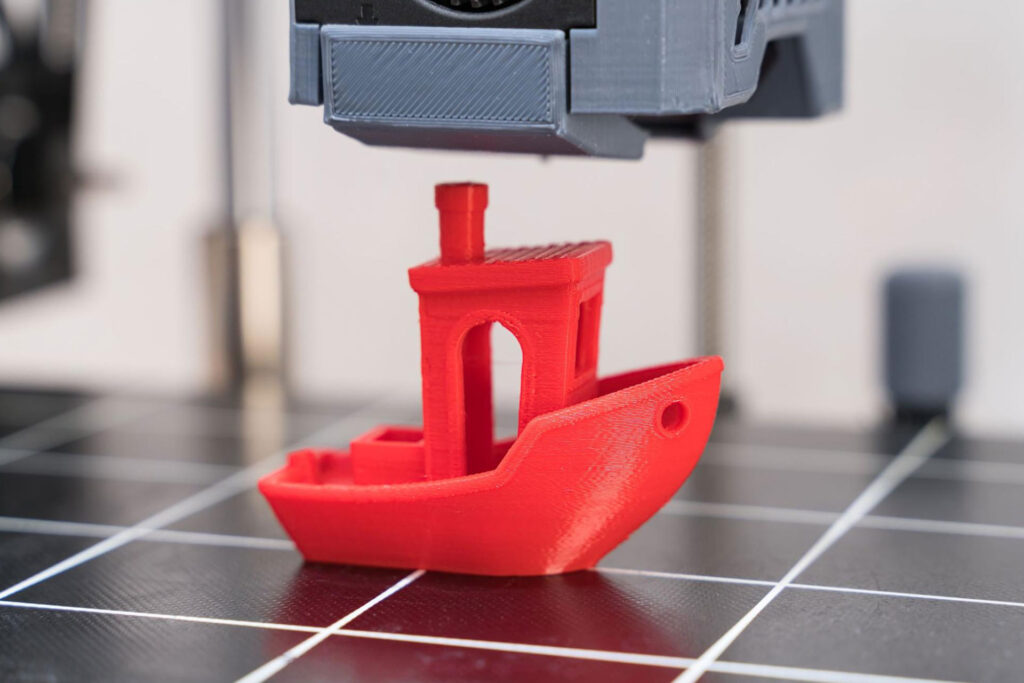

How Do 3D Printers Work?
Essentially, 3D Printers follow a specific operational routine, which includes:
1. Digital Modeling: A digital 3D model acts as the blueprint and source of the physical item. This model is effectively divided into numerous horizontal layers, a task orchestrated by the appropriate software.
2. Layer Preparation: Each layer is individually prepared and readied for printing. The preparation involves identifying the sequence of movement and depositing of material.
3. Printing Process: Layer-by-layer, the 3D printer executes the planned sequence. The printer’s nozzle transverses through predetermined coordinates, depositing or solidifying the material in the process.
4. Sequential Addition: The nozzle’s movement and material addition are replicated as per the earlier specified patterns. Each layer is stocked onto the other sequentially which gradually takes the form of the intended object.
5. Accurate Creation: This repeated process eventually results in the formation of an accurate and comprehensive three-dimensional object as per the original digital model.
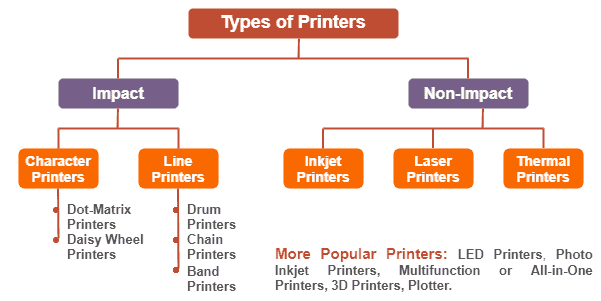
Which Materials Do 3D Printers Use to Create Things?
The list of materials utilized in 3D printing is extensive and ever-growing. Each material has its unique properties, advantages and limitations which suit specific applications. Let's take a closer look at these materials and their defining characteristics:
- Thermoplastics: The most widely used materials in 3D printing, thermoplastics like ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) and PLA (Polylactic Acid) are appreciated for their flexibility, durability and affordability. With their ability to be easily melted and reshaped, they are an excellent option for a multitude of applications.
- Metals: For high-strength and precision applications, metals such as titanium, stainless steel, and even precious metals like gold and silver are employed. Metal 3D printing is commonly used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical, and jewelry manufacturing.
- Resin: Resin is used in Stereolithography (SLA) 3D printers. The liquid photosensitive resin hardens under a UV light source to form the layers. It is favored due to its high-detail output and smooth surface finishes, making it suitable for detailed models and castable jewelry.
- Ceramics: Although more challenging to work with, ceramics are valued for their hardness, heat resistance, and aesthetic qualities. These properties make them ideal for artistic works and complex geometries.
- Nylon: Its strength, flexibility, and excellent wear resistance make nylon a great option for moving parts, mechanical components, and strong, flexible prototypes.
- Sandstone: The only full-color 3D printable material which is actually a gypsum-based binder with colored ink. It's usually used in architecture, figurines, and complex decorative models.
The choice of material largely depends on the intricacy of the design, durability required, and the application of the 3D printed object. In the rapidly evolving field of 3D printing, new materials are continually being developed and tested to expand the possibilities.
What Are Some Real-World Applications of 3D Printing Materials?
The broad spectrum of materials compatible with 3D printing technology has made it an instrumental tool across various industries. Let's delve into some practical uses of these materials:
1. Thermoplastics in Consumer Goods: Thermoplastics are routinely used in the production of everyday items such as toy models, smartphone cases, and kitchen utensils. Their ease of use, durability and moldability make them ideal for cost-effective large-scale production.
2. Biodegradable PLA (Polylactic Acid) in Eco-friendly Solutions: PLA, a biodegradable thermoplastic derived from renewable resources like corn starch or sugarcane, is widely valued for its sustainability factor. It has claimed its place in producing eco-sensitive products, such as biodegradable containers and reusable shopping bags.
3. Metals in Aerospace and Automotive Industry: The strength and heat resistance of metals, such as titanium and stainless steel, makes them a top choice for 3D printing in these industries. They're commonly employed in manufacturing engine parts for cars and spacecraft.
4. Ceramics in Dental Industry: Dental professionals widely use ceramics to create crowns, bridges, and veneers due to their pristine aesthetics and high durability.
5. Resins in Medical Field: In the medical sphere, safe, biocompatible resin is used to create surgical guides, teaching aids, and prototypes.
To sum up, the choice of material in 3D printing depends largely on its intended use. As we continue to innovate and push the boundaries of this technology, the applications of these materials will undoubtedly expand.
Where Is The Future Headed For 3D Printing?
The future possibilities of 3D printing are limitless. This revolutionary technology continues to redefine customization, sustainability, and speed in manufacturing. Below are some key areas where 3D printing technology is expected to make significant strides:
- Biomedical Applications: 3D printing is poised to stir a revolution in healthcare by facilitating the production of custom implants, prosthetics, and even body organs using patient-specific data. It is predicted that by 2024, the market value for 3D printed medical products will reach $2.31 billion.
- Aerospace and Automotive Industries: For these sectors, lightweight, durable metallic 3D printed parts are a boon. They enhance efficiency by reducing fuel consumption and lowering emissions. For instance, The European Space Agency's 3D-printed metal rocket engine has shown promising results.
- Sustainable Manufacturing: 3D printing promotes sustainability by reducing waste and energy use. It can utilize recycled material, making it a green manufacturing solution.
- Food Industry: There's a niche market growing around 3D food printing capable of customizing nutritional content and producing intricate designs impossible by hand.
- Personalized Apparel: Customized clothing and footwear made using 3D printing could become a norm, enhancing customer satisfaction.
By harnessing the potentials of various materials and developing new ones, the future appears bright for the world of 3D printing.
Conclusion
3D printing is transforming numerous industries. In healthcare, biocompatible materials are used for making personalized prosthetics and implants. In aerospace and automotive, metals are used to create light, strong components. In architecture, sandstone-like materials allow for producing precise scale models. The fashion industry also utilizes 3D printing for creating intricate and bespoke items from polymers and nylon.
Related FAQs about what do 3d printers use to make things
What determines the material choice for a particular 3D printing project?
The choice of material for a 3D printing project depends on various factors. These include the intended use of the printed object, the required strength and durability, as well as the desired finish. For instance, metals are preferred for parts that need high strength, whereas thermoplastics might be the choice for prototypes or custom objects.
What is the role of software in 3D printing?
Software plays a crucial role in 3D printing. It is used to design the 3D model, and to slice the model into the many layers that the printer will fabricate step-by-step. The software also controls the movements of the printer, and the deposition or solidification of the material.
Are there any environmental concerns associated with 3D printing materials?
Yes, there are environmental concerns with some 3D printing materials. While certain materials like PLA are biodegradable, others like ABS are not. Emissions from melting some materials can also be harmful. However, because 3D printing typically reduces material waste and can use recycled materials, it also has potential environmental benefits.